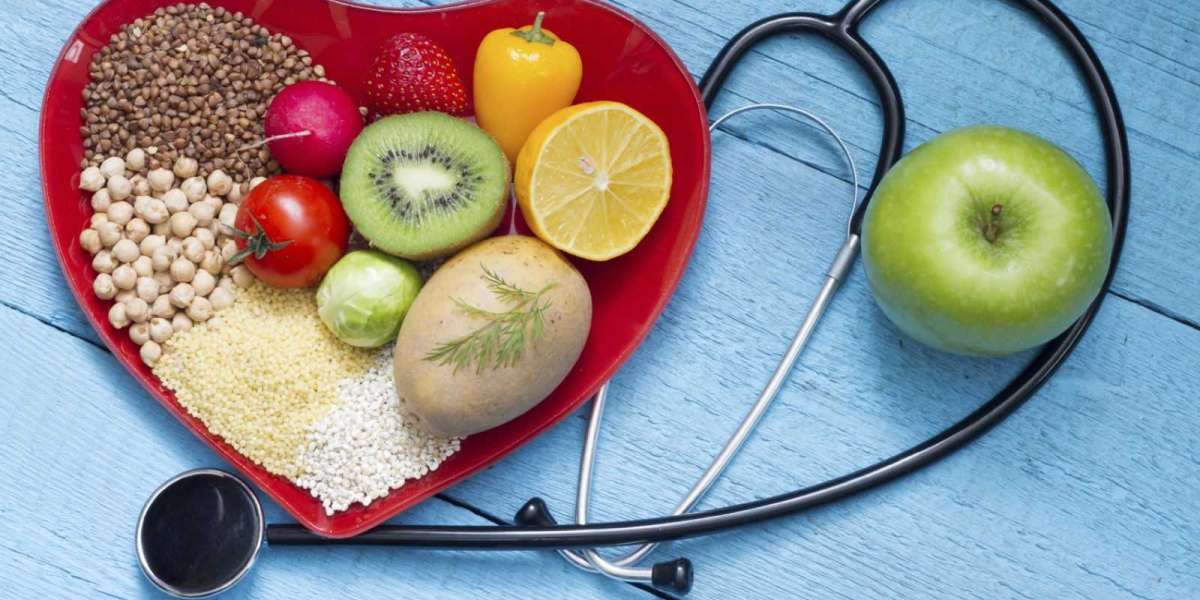
Cholesterol is a type of lipid (fat) that is essential for various bodily functions such as building cell membranes, producing hormones, and aiding in digestion. However, high levels of cholesterol in the blood can increase the risk of heart disease and stroke. In this article, we will explore the different types of cholesterol, their functions in the body, the causes and effects of high cholesterol levels, and ways to manage cholesterol.
Types of Cholesterol
There are two main types of cholesterol: LDL (low-density lipoprotein) and HDL (high-density lipoprotein). LDL is often referred to as "bad" cholesterol, while HDL is considered "good" cholesterol.
LDL Cholesterol
LDL is responsible for transporting cholesterol from the liver to the rest of the body, where it can be used to build cell membranes and produce hormones. However, when there is too much LDL in the bloodstream, it can form plaques in the walls of the arteries, leading to atherosclerosis (hardening and narrowing of the arteries) and increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
HDL Cholesterol
HDL, on the other hand, helps remove excess cholesterol from the bloodstream and transport it back to the liver for processing and elimination. This is why HDL is considered "good" cholesterol.
Functions of Cholesterol
As mentioned earlier, cholesterol plays several important roles in the body.
Here are some of its functions:
Building cell membranes: Cholesterol is a key component of cell membranes, which are responsible for protecting the cell and regulating its internal environment.
Producing hormones: Cholesterol is a precursor to several hormones, including estrogen, testosterone, and cortisol.
Digestion: Cholesterol helps in the digestion of fat-soluble vitamins, such as vitamins A, D, E, and K.
Causes and Effects of High Cholesterol Levels
High cholesterol levels can be caused by a combination of factors, which includes:
- Diet:
The foods we eat play a significant role in our cholesterol levels. Foods high in saturated and trans fats can raise LDL (low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol levels in the blood. Examples of such foods include fatty meats, full-fat dairy products, fried foods, baked goods, and processed snacks.
- Genetics:
Genetics also plays a role in cholesterol levels. Familial hypercholesterolemia is an inherited condition that causes very high levels of LDL cholesterol in the blood. It is caused by mutations in the genes that regulate cholesterol metabolism. People with this condition have a higher risk of developing heart disease at an early age.
- Sedentary Lifestyle:
Physical inactivity can lead to high cholesterol levels. Regular exercise helps to increase HDL (high-density lipoprotein) cholesterol levels in the blood, which can help to reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Obesity:
Being overweight or obese can also increase cholesterol levels. Excess body fat can lead to insulin resistance, which can cause LDL cholesterol levels to rise.
- Age and Gender:
As we age, our cholesterol levels tend to increase. Women typically have lower cholesterol levels than men until they reach menopause. After menopause, women's LDL cholesterol levels tend to increase.
- Smoking:
Smoking damages the walls of the blood vessels, making it easier for cholesterol to stick to them. This can lead to the buildup of plaque in the arteries and increase the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Health Conditions:
Certain health conditions can also increase cholesterol levels, including diabetes, kidney disease, liver disease, and an underactive thyroid gland.
Here are some of the effects of high cholesterol levels:
Atherosclerosis: High levels of LDL cholesterol can lead to the buildup of plaques in the arteries, which can increase the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Heart disease and stroke: The buildup of plaques in the arteries can restrict blood flow to the heart and brain, leading to heart attacks and strokes.
Peripheral artery disease: High cholesterol levels can also lead to peripheral artery disease, which is the narrowing of the arteries that supply blood to the legs and arms.
How to Lower Cholesterol
High cholesterol levels can increase the risk of heart disease and stroke, but there are several lifestyle changes and treatments that can help lower cholesterol levels. In this article, we will explore various methods to lower cholesterol levels.
- Diet Changes:
Dietary changes are one of the most effective ways to lower cholesterol levels.
Here are some tips to help reduce cholesterol levels through dietary changes:
a) Reduce Saturated and Trans Fats: Saturated and trans fats raise LDL cholesterol levels in the blood. Foods high in saturated fats include fatty meats, butter, cream, and cheese. Trans fats are found in processed foods such as baked goods, fried foods, and snack foods. Reducing the intake of these foods can help lower cholesterol levels.
b) Increase Fiber Intake: Soluble fiber can help reduce cholesterol levels by binding to cholesterol in the digestive system and removing it from the body. Foods high in soluble fiber include fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains.
c) Eat More Healthy Fats: Foods containing healthy fats, such as omega-3 fatty acids and monounsaturated fats, can help raise HDL cholesterol levels in the blood. Sources of healthy fats include fatty fish, avocados, nuts, and olive oil.
- Exercise:
Regular exercise can help lower cholesterol levels by raising HDL cholesterol levels in the blood. It also helps maintain a healthy weight, which can also help lower cholesterol levels. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week.
- Weight Management:
Being overweight or obese can increase LDL cholesterol levels in the blood. Losing weight through diet and exercise can help lower cholesterol levels.
- Quit Smoking:
Smoking damages the walls of the blood vessels, making it easier for cholesterol to stick to them. Quitting smoking can help lower cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Medications:
If lifestyle changes are not enough to lower cholesterol levels, medications such as statins may be prescribed by a doctor. Statins work by reducing the production of cholesterol in the liver. Other medications may also be prescribed to help lower cholesterol levels.
Conclusion
cholesterol plays a vital role in the body, but high levels of LDL cholesterol can increase the risk of heart disease and stroke. By adopting healthy lifestyle habits and working with a doctor to manage cholesterol levels, it is possible to reduce the risk of these conditions and maintain overall health.


Emmanuel Frank 1 와이
Wow